This article is the third in a series about AI and how you can begin to think about and leverage the various AI technologies. Last time we talked about the importance of good data when building and training AI models. Today we are going to take a deeper look at the different functional categories of AI and talk about how these different types of AI can be used in your day to day business activities. Once we cover the different types, we will go a step further to uncover the different use cases and capabilities provided by the various Salesforce products. That will be done across several follow-up articles. For now though, let’s have a look at the different types of AI categories and capabilities.
At a high level, there are four different progressions of AI systems or applications, and this can serve as a starting categorization. Note that not all of these have been fully realized yet.
1. Reactive AI:
These systems operate based on predefined rules and don’t possess memory or the ability to learn from past experiences. They respond to specific inputs without any understanding of context. While limited in their scope, they’re often used in tasks where specific responses are required, such as a chatbot which runs through a predefined script and decision tree.
2. Limited Memory AI:
Unlike reactive AI, these systems can learn from historical data to make informed decisions. They have a limited memory capacity to store past experiences, allowing them to improve performance over time. ChatGPT is a good example, as it does not retain information about past interactions beyond a certain window. Self-driving cars are another example where they are able to anticipate and react to changing traffic conditions.
3. Theory of Mind AI:
This is a hypothetical level of AI that doesn’t exist yet in its full form. This is a level of AI that would have the ability to understand human emotions, beliefs, intentions, and thought processes. AI does not currently possess true empathy or understanding of human emotions. This is generally considered the next frontier of AI development.
4. Self-Aware AI:
This type represents AI systems that have consciousness and self-awareness, understanding their own existence and emotions. This level of AI is largely theoretical and remains a subject of philosophical debate.
AI systems can also be broken into Narrow AI (also known as Weak AI) and General AI classifications. A Narrow or Weak AI system is built for a very specific and highly-focused task or set of tasks. Think chess playing algorithms, smartphone assistants like Siri, and self-driving cars. A General AI system is built to be broad and adaptable, able to think and function like humans do, and be capable of unsupervised learning. You may hear the term Artificial General Intelligence, or AGI, when referring to General AI systems. This concept is actively being worked on, but like Theory of Mind and Self Aware AI, we have not yet built a General AI system.

While the academic classifications introduced above are certainly interesting and provide plenty of ideas to ponder on, there are other broad functional categories of AI capabilities that are more useful in practice, when talking about tools and algorithms which are actually available right now (as opposed to purely theoretical categories). Two of these broader categories are Predictive AI and Generative AI. These are the categories you are most likely to encounter at the moment as you work to incorporate AI into your business technology strategy. These terms will come up over and over again so it is important to understand what they mean and how they differ from one another.
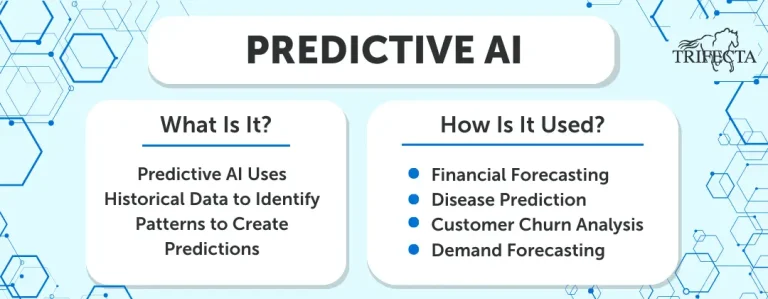
Predictive AI is the older of the two categories. Humans have been using statistical analysis to make predictions for a very long time, and once computers were powerful enough and enough historical data was available, this became one of the first areas of application of Artificial Intelligence principles and concepts. Predictive AI essentially takes large amounts of historical data and uses algorithms to identify patterns in that data and then make predictions about future events or outcomes. That is a very simplistic explanation of what happens, of course. We will have a closer look at the underlying concepts and technologies in a follow-up article.
The applications of Predictive AI are many and span various industries, including finance, healthcare, sales, marketing, and manufacturing. Predictive AI models can be used for financial forecasting, disease prediction, customer churn analysis, demand forecasting, and many other use cases. It is a powerful tool to enable you to make informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
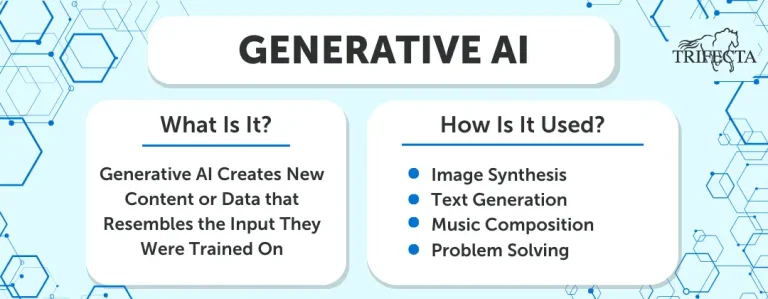
Generative AI is the category you have probably heard the most about recently. Specifically, ChatGPT has got an enormous amount of press coverage since its release by OpenAI in November 2022. It’s hard to believe it has only been a year since its release with everything we continue to hear about it. Generative AI applications like ChatGPT focus on creating new content or data that resembles the input they were trained on. The content can be images, text, audio, or even other forms of data. The primary goal is to generate content that is indistinguishable from what a human might produce. Huge data sets are used to train the models behind these applications. Like Predictive AI, we will go into more detail on how this works in the coming weeks.
Generative AI capability and “realism” has grown leaps and bounds over the past few years due to the ability of massively large data sets to train with (for example, all publicly available content on the internet), an increase in the efficiency and accuracy of the algorithms used, and large amounts of computing power that is much more affordable than it was just a few years back. As available training data and compute power grows, so will the capabilities of the applications.
Generative AI is currently being applied to solve many different problems, including image synthesis, text generation, music composition, and more.
Two other categories that you may encounter help support both Generative and Predictive AI. These are Natural Language Processing, or NLP, and Computer Vision AI. We will not dive into these quite as deeply as we do with Predictive and Generative AI in the upcoming articles, but it is good to understand what these are.
NLP-based AI focuses on understanding, interpreting, and generating human language. ChatGPT actually uses NLP to process the instructions – known as prompts – that you feed it, and then uses the outcome of that NLP step to feed the transformer model which generates the output text. Other applications of NLP include language translation, sentiment analysis, chatbots and language generation.
Computer Vision AI involves teaching machines to interpret and understand the visual world. It includes tasks like object recognition, image classification, and image generation. This capability is being used in areas such as surveillance, healthcare, and autonomous systems, but it also is utilized as part of Generative AI applications which create images, to ingest, classify and refine both the training and output data.
In the next article, we will delve more into Predictive AI and look at the various Salesforce offerings in the Predictive AI space, and then will go further into Generative AI in the article after that. In the meantime, if you want to learn more about the different AI capabilities that the Salesforce platform provides, or get in touch and the experts at Trifecta will be happy to help guide you along your journey.